# 前言
本次主要使用 Seurat 比较 STAR 与 Cellranger 的输出结果,只会进行简单的聚类工作。
# 数据读入
> library (Seurat) | |
> library (dplyr) | |
> library (magrittr) | |
> library (gtools) | |
> library (stringr) | |
> library (Matrix) | |
> setwd ("D://data/ScRNAcode") | |
## 读入 STAR 数据 | |
> matrix.dir="STAR/" | |
> barcode.path <- paste0 (matrix.dir,"barcodes.tsv") | |
> features.path <- paste0 (matrix.dir,"features.tsv") | |
> matrix.path <- paste0 (matrix.dir, "matrix.mtx") | |
> STARmatrix <- readMM (file = matrix.path) | |
> feature.names = read.delim (features.path, | |
+ header = FALSE, | |
+ stringsAsFactors = FALSE) | |
> barcode.names = read.delim (barcode.path, | |
+ header = FALSE, | |
+ stringsAsFactors = FALSE) | |
> colnames (STARmatrix) = barcode.names$V1 | |
> rownames (STARmatrix) = feature.names$V2 | |
> STARmatrix<-as.matrix (STARmatrix) | |
> STARmatrix [1:6,1:6] | |
## 创建 seurat 对象 | |
## 创建 STAR 的 Seurat 对象 | |
> STAR <- CreateSeuratObject (STARmatrix,project = "zsz", | |
min.cells = 3, min.features = 200) | |
## 创建 Cellranger 的 Seurat 对象 | |
> dir="cellranger/" | |
> counts <- Read10X (data.dir = dir) | |
> RANGER <- CreateSeuratObject (counts, project = "zsz", | |
min.cells=3, min.features = 200) |
# 数据比较
> ## 数据比较 | |
> dim (STARmatrix) | |
[1] 33538 2048 | |
> dim (counts) | |
[1] 33538 2112 | |
> dim (STAR) | |
[1] 13350 2046 | |
> dim (RANGER) | |
[1] 13314 2105 | |
> fivenum (apply (STARmatrix,1,function (x) sum (x>0))) | |
MIR1302-2HG IGFBPL1 AL008723.2 FXYD7 MT-CO1 | |
0 0 0 29 2047 | |
> fivenum (apply (counts,1,function (x) sum (x>0))) | |
MIR1302-2HG FAM221B LINC01638 DGKE MT-CO1 | |
0 0 0 29 2108 | |
> pdf ("box.pdf",height = 9,width = 9) | |
> boxplot (apply (STARmatrix,1,function (x) sum (x>0) ),main = "STAR",col = "lightgray") | |
> boxplot (apply (counts,1,function (x) sum (x>0) ),main = "Cellranger",col = "lightgray") | |
> dev.off () | |
RStudioGD | |
2 | |
> pdf ("hist.pdf",height = 9,width = 9) | |
> hist (apply (STARmatrix,2,function (x) sum (x>0) ),col = "lightgray", | |
+ breaks=20,xlim=c (0,4000),ylim=c (0,800), | |
+ labels=F,main="STAR", | |
+ xlab="genes",ylab="cells") | |
> abline (v=median (apply (STARmatrix,2,function (x) sum (x>0))),col='red') | |
> hist (apply (counts,2,function (x) sum (x>0) ),col = "lightgray", | |
+ breaks=20,xlim=c (0,4000),ylim=c (0,800), | |
+ labels=F,main="Cellranger", | |
+ xlab="genes",ylab="cells") | |
> abline (v=median (apply (counts,2,function (x) sum (x>0))),col='red') | |
> dev.off () |
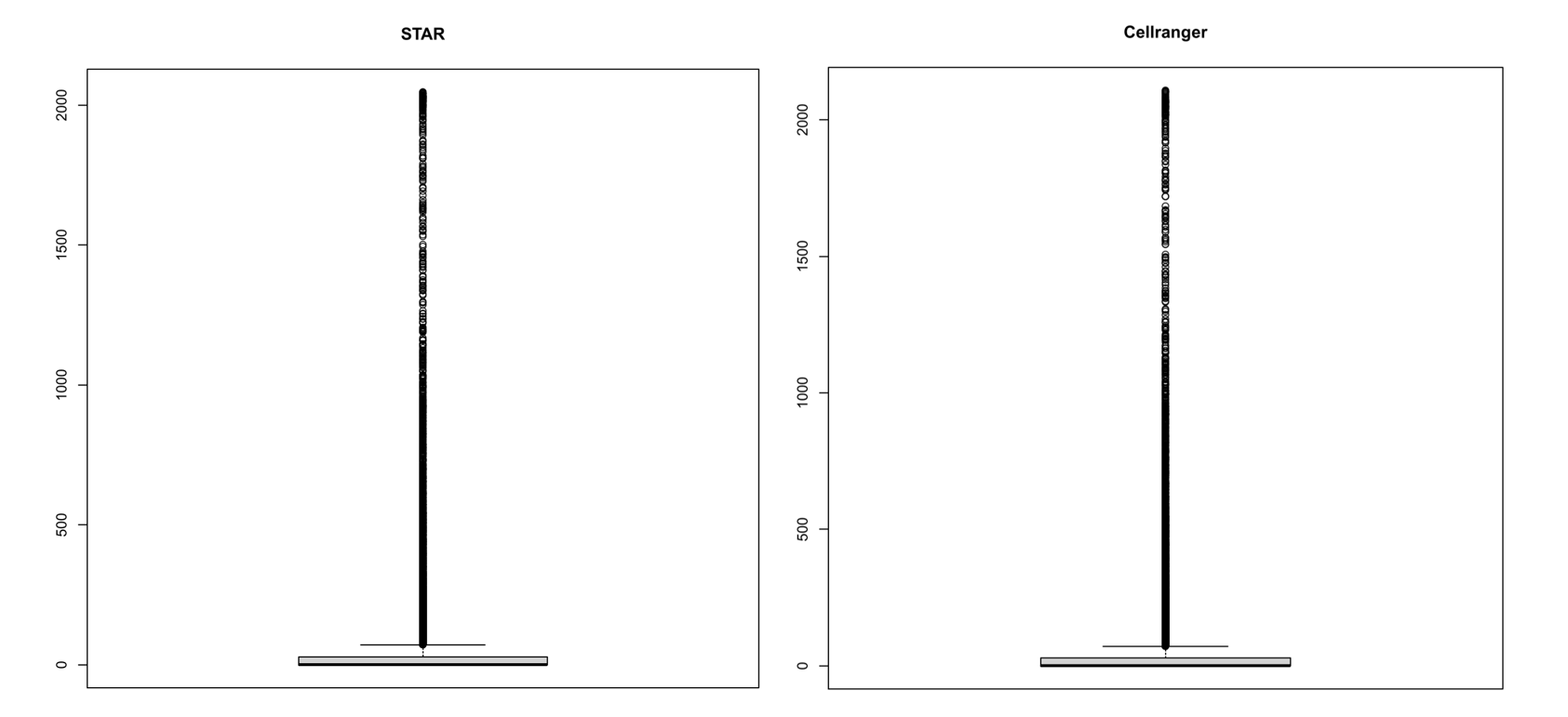
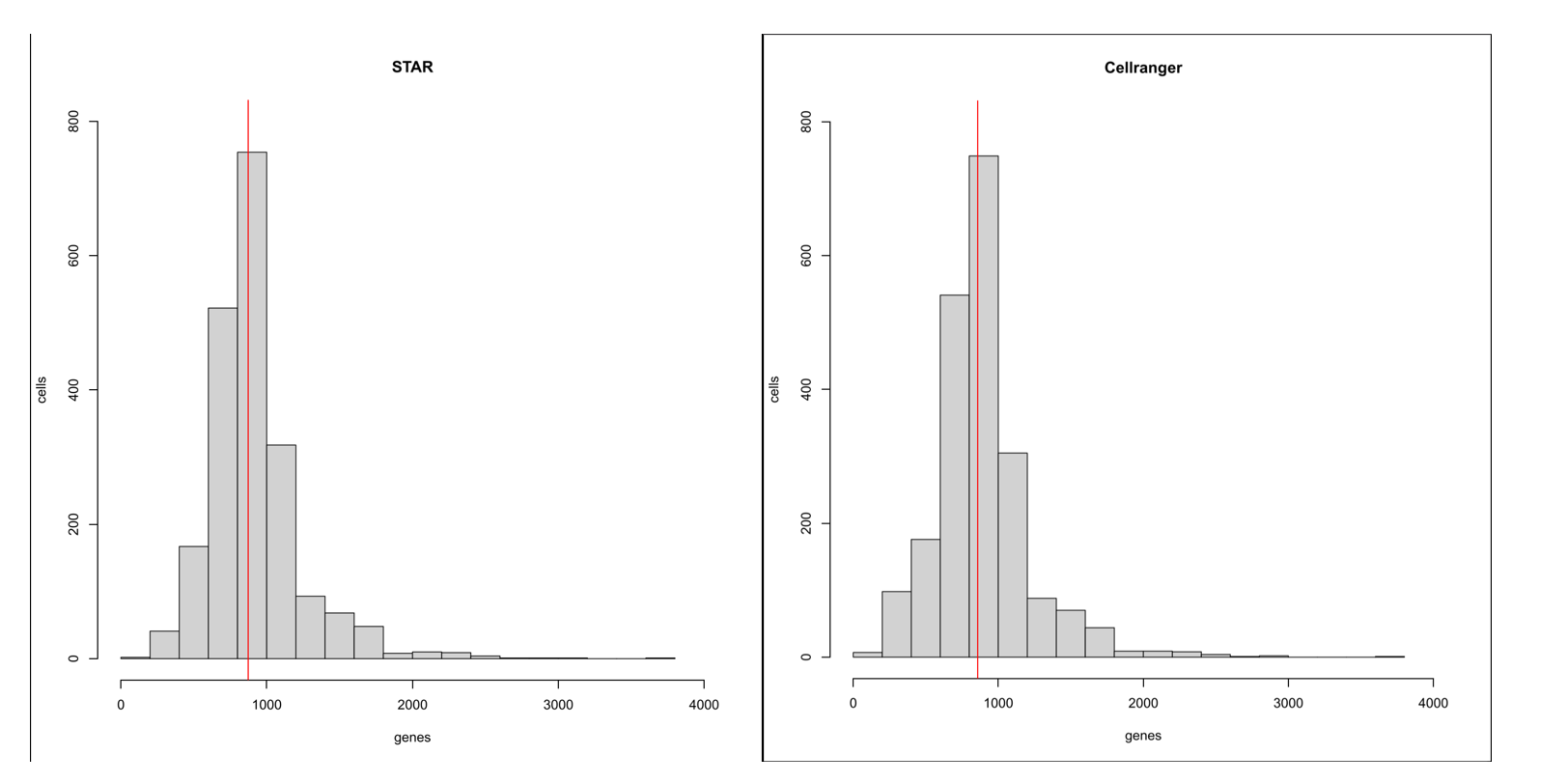
根据箱线图,直方图和矩阵的基本信息,可以看到 STAR 与 cellranger 的结果差距很小
# 质量控制与聚类比较
> pdf("qc.pdf",height = 9,width = 9) | |
> VlnPlot(STAR, | |
+ features = c("nFeature_RNA", "nCount_RNA"), | |
+ pt.size = 0.1, | |
+ ncol = 2) | |
> VlnPlot(RANGER, | |
+ features = c("nFeature_RNA", "nCount_RNA"), | |
+ pt.size = 0.1, | |
+ ncol = 2) | |
> dev.off() | |
RStudioGD | |
2 |
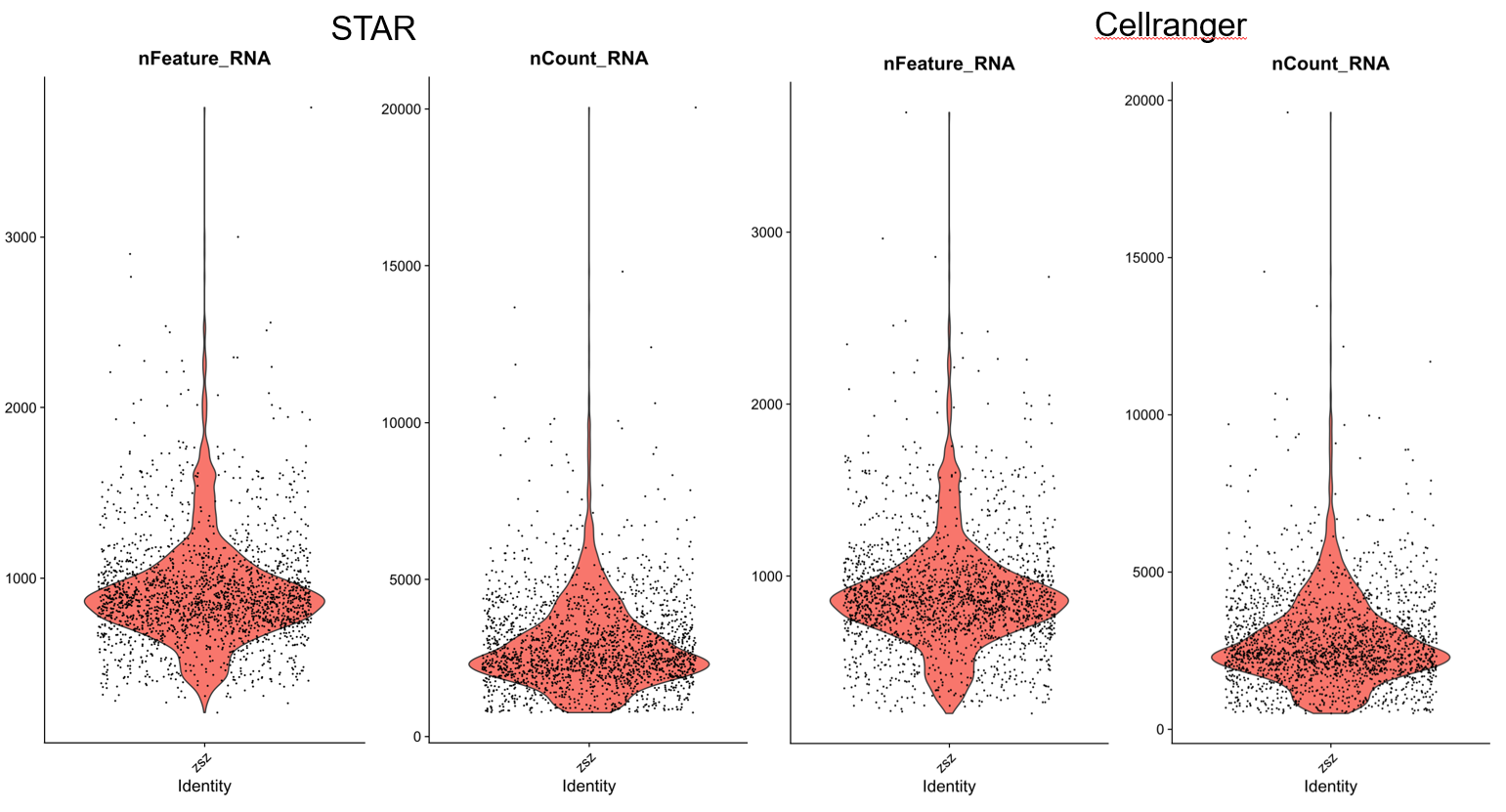
> STAR<-subset(STAR,subset=nFeature_RNA>500 & nFeature_RNA<2000) | |
> STAR <- NormalizeData(STAR, normalization.method = "LogNormalize", scale.factor = 10000) | |
Performing log-normalization | |
0% 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100% | |
[----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----| | |
**************************************************| | |
> table(STAR@meta.data$orig.ident) | |
zsz | |
1896 | |
> STAR <- FindVariableFeatures(STAR, selection.method = "vst", nfeatures = 2000) | |
Calculating gene variances | |
0% 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100% | |
[----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----| | |
**************************************************| | |
Calculating feature variances of standardized and clipped values | |
0% 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100% | |
[----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----| | |
**************************************************| | |
> top10 <- head(VariableFeatures(STAR), 10) | |
> top10 | |
[1] "S100A9" "S100A8" "IGLC2" "IGKC" "LYZ" "IGLC3" "CCL3" "NFKBIA" "PTGDS" "S100A12" | |
> RANGER<-subset(RANGER,subset=nFeature_RNA>500 & nFeature_RNA<2000) | |
> RANGER<- NormalizeData(RANGER, normalization.method = "LogNormalize", scale.factor = 10000) | |
Performing log-normalization | |
0% 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100% | |
[----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----| | |
**************************************************| | |
> table(RANGER@meta.data$orig.ident) | |
zsz | |
1895 | |
> RANGER <- FindVariableFeatures(RANGER, selection.method = "vst", nfeatures = 2000) | |
Calculating gene variances | |
0% 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100% | |
[----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----| | |
**************************************************| | |
Calculating feature variances of standardized and clipped values | |
0% 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100% | |
[----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----| | |
**************************************************| | |
> top10 <- head(VariableFeatures(RANGER), 10) | |
> top10 | |
[1] "S100A9" "S100A8" "IGLC2" "IGKC" "LYZ" "CCL3" "NFKBIA" "IGLC3" "PTGDS" "S100A12" | |
> scale.genes <- rownames(STAR) | |
> STAR <- ScaleData(STAR, features = scale.genes) | |
> STAR <- RunPCA(STAR, features = VariableFeatures(STAR)) | |
> plot1 <- ElbowPlot(STAR, ndims=30, reduction="pca") | |
> scale.genes <- rownames(RANGER) | |
> RANGER <- ScaleData(RANGER, features = scale.genes) | |
> RANGER <- RunPCA(RANGER, features = VariableFeatures(RANGER)) | |
> plot2 <- ElbowPlot(RANGER, ndims=30, reduction="pca") | |
> plotc <- plot1+plot2 | |
> ggsave("pca.pdf", plot = plotc, width = 8, height = 4) |
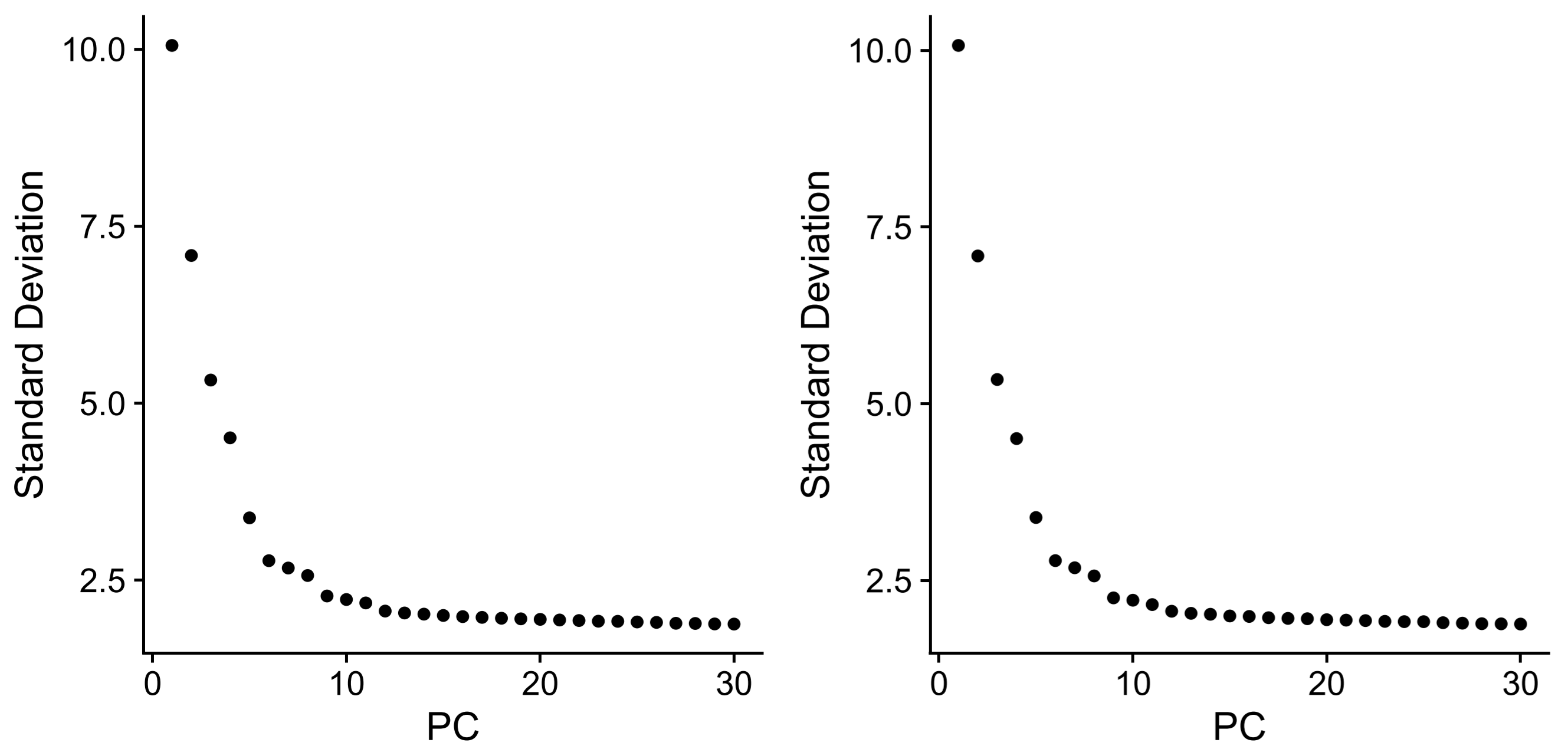
> STAR <- FindNeighbors(STAR, dims = 1:10) | |
> STAR <- FindClusters(STAR, resolution = 0.8) | |
> table(STAR@meta.data$seurat_clusters) | |
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | |
368 310 290 217 184 129 119 112 92 75 | |
> metadata <- STAR@meta.data | |
> cell_cluster <-data.frame(cell_ID=rownames(metadata), | |
cluster_ID=metadata$seurat_clusters) | |
> STAR <- RunUMAP(STAR, dims = 1:20) | |
> embed_tsne <- Embeddings(STAR, 'umap') | |
> plot1 = DimPlot(STAR, reduction = "umap" ,label = "T", pt.size = 1,label.size = 4) | |
> RANGER <- FindNeighbors(RANGER, dims = 1:10) | |
> RANGER <- FindClusters(RANGER, resolution = 0.8) | |
> table(RANGER@meta.data$seurat_clusters) | |
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | |
375 300 290 212 195 128 122 108 91 74 | |
> metadata <- RANGER@meta.data | |
> cell_cluster <- data.frame(cell_ID=rownames(metadata), cluster_ID=metadata$seurat_clusters) | |
> RANGER <- RunUMAP(RANGER,n.neighbors = 30,dims = 1:20) | |
> embed_umap <- Embeddings(RANGER, 'umap') | |
> plot2 = DimPlot(RANGER, reduction = "umap" ,label = "T", pt.size = 1,label.size = 4) | |
> plotc <- plot1+plot2 | |
> ggsave("umap.pdf", plot = plotc, width = 8, height = 4) |
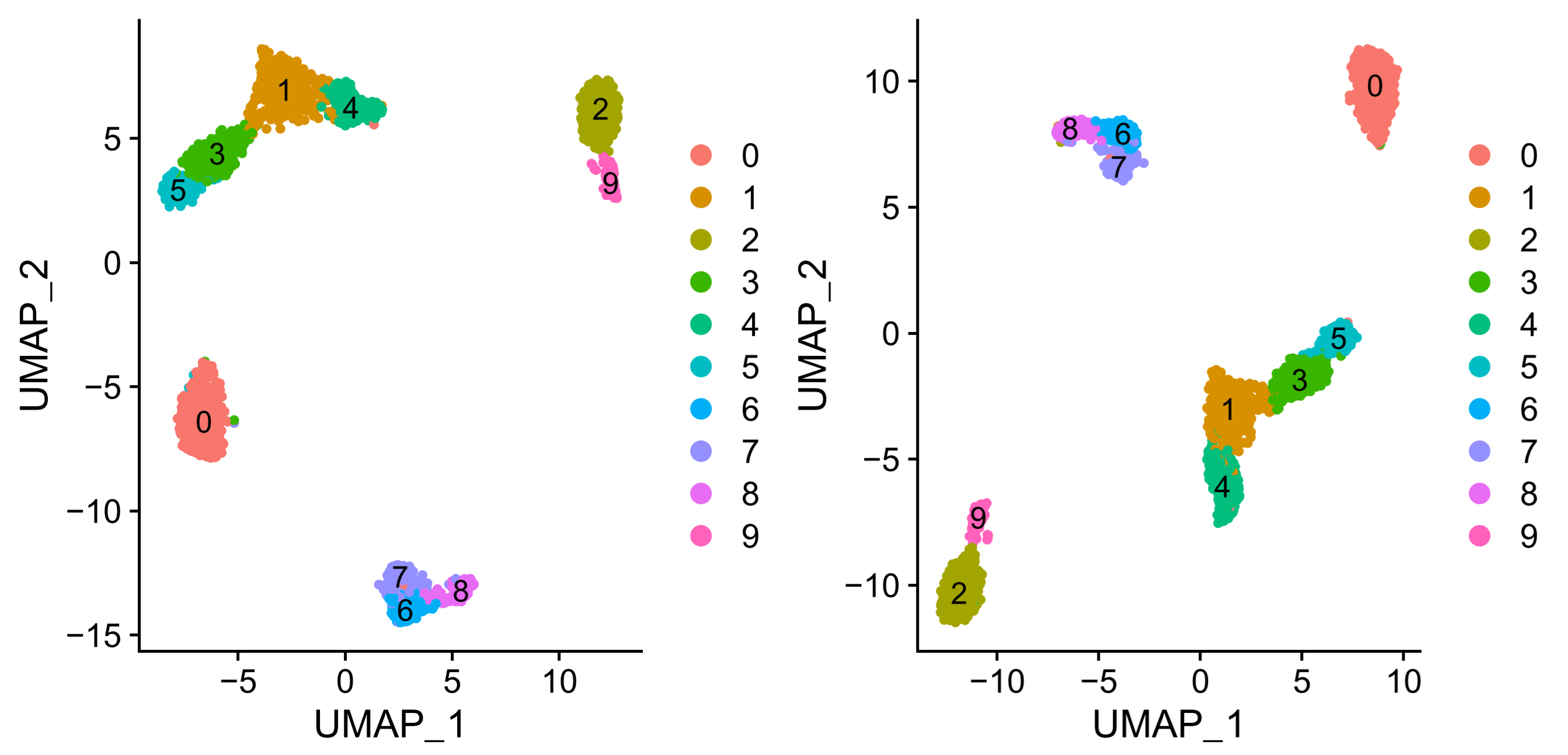
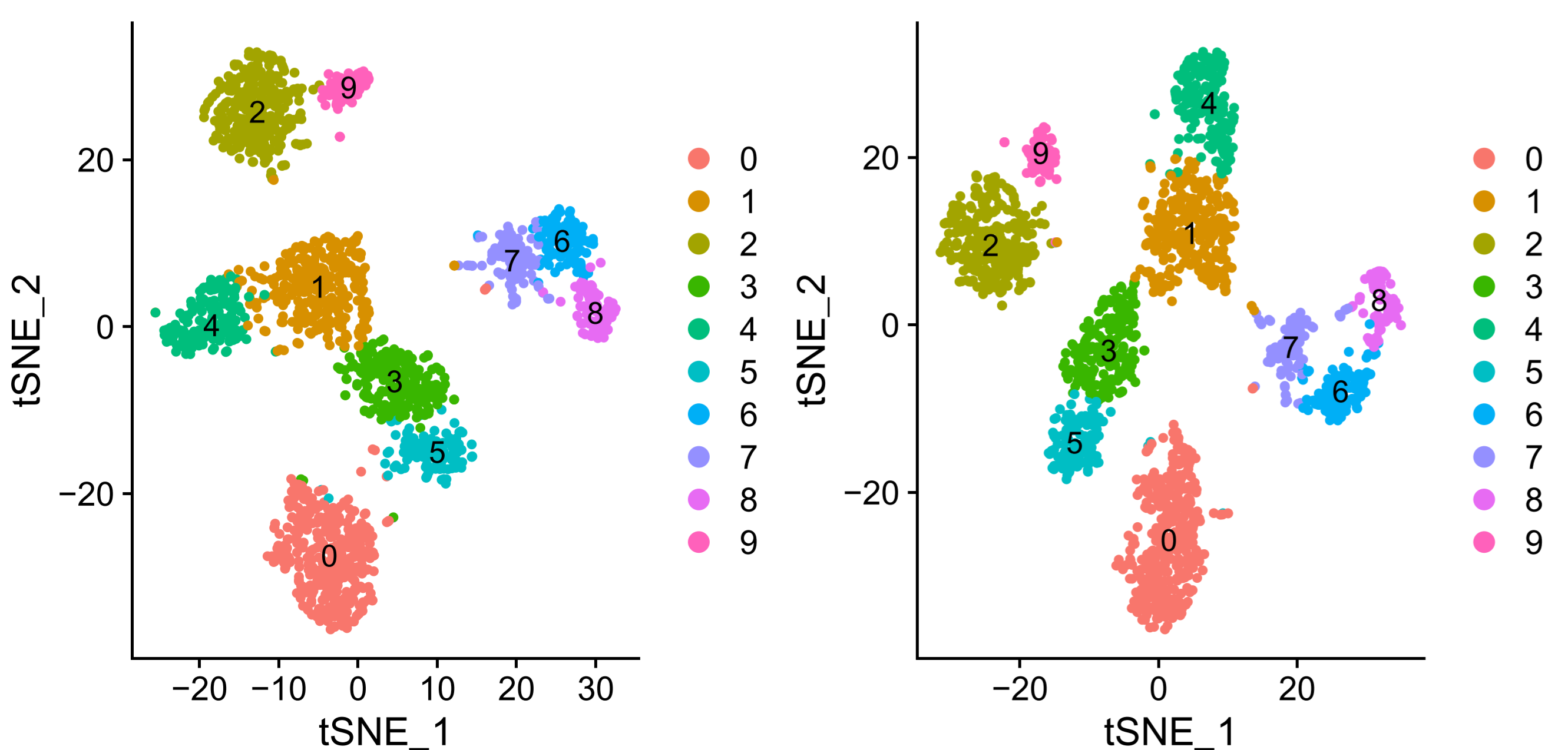
可以看到两种分析方法 umap 与 tsne 聚类效果不太相同,但是基本的聚类与分群是一致的
# 结语
就结果而言,两种分析方法的结果不完全相同,但也基本一致,本次笔记中用到的数据和代码已上传 github,在 ScRNAseq_code/compare 文件夹下,大家需要的可以下载试试